What Causes The Onset Of Adhd
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects about 11% of children in the United States. It is characterized by symptoms such as inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. Researchers have been studying the causes of ADHD for many years, and while there is no single identified cause, there are several factors that may contribute.
The Genetics of ADHD
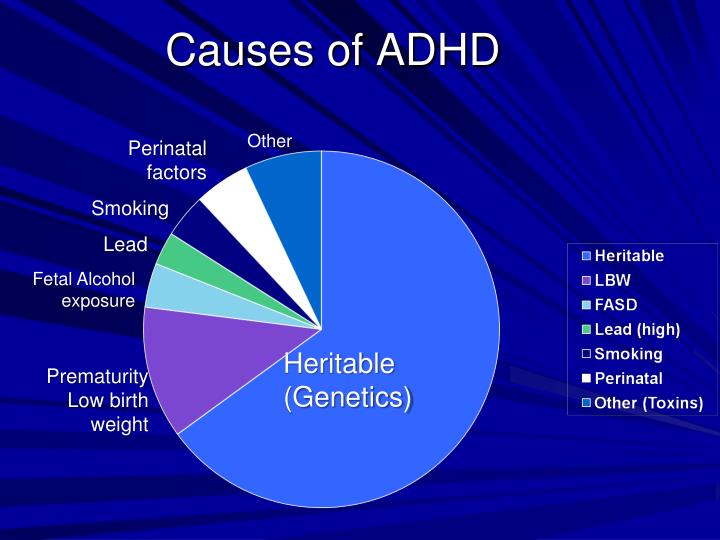
One significant factor in the development of ADHD is genetics. Studies have shown that ADHD tends to run in families, suggesting that there is a genetic component to the disorder. Children who have a parent or sibling with ADHD are at a higher risk of developing the condition themselves. Research has also identified specific genes that are associated with ADHD, although the exact genetic mechanisms are not well understood.
Brain Structure and Function
Another factor that may contribute to the development of ADHD is differences in brain structure and function. Research has suggested that certain areas of the brain, such as the prefrontal cortex, may be smaller in individuals with ADHD. This part of the brain is responsible for executive functions such as attention, planning, and working memory. Additionally, differences in neurotransmitter function, specifically in the dopamine and norepinephrine systems, have been implicated in ADHD.
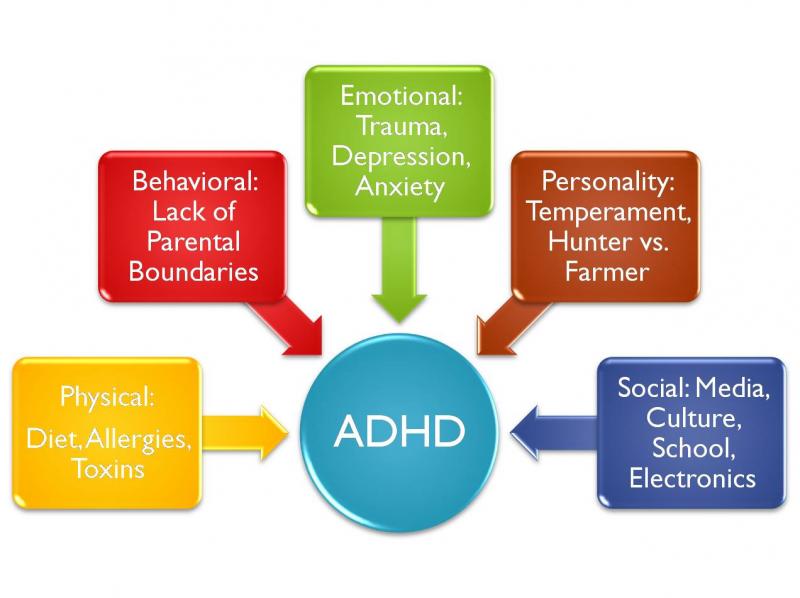
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as prenatal and postnatal exposures to toxins, premature birth, low birth weight, and maternal stress have also been studied as potential contributors to ADHD. Research has found that exposure to lead, polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs), and pesticides have been associated with an increased risk of ADHD. Additionally, studies have shown that maternal stress during pregnancy and early childhood may increase the likelihood of a child developing ADHD.
Treatment Options
While the causes of ADHD are complex and multifaceted, there are treatments available that can help manage the symptoms of the disorder. Medications such as stimulants and non-stimulants can improve focus and reduce impulsivity and hyperactivity. Behavioral therapy, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and parent training, can help individuals with ADHD develop coping skills and improve their social interactions. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, adequate sleep, and a healthy diet can also help manage symptoms of ADHD.
Conclusion
ADHD is a complex disorder that arises from a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurobiological factors. While the exact causes of ADHD are not fully understood, researchers continue to explore various factors that may contribute to the development of the condition. With proper treatment, individuals with ADHD can lead successful and fulfilling lives.