What Can An Ear Infection Cause
Ear infections are a common condition that can affect people of all ages. They can be caused by a variety of factors, such as bacteria, viruses, or allergies. What you may not know is that ear infections can also cause jaw pain. In this article, we will explore the connection between ear infections and jaw pain and what you should know about this condition.
What Causes Ear Infections?
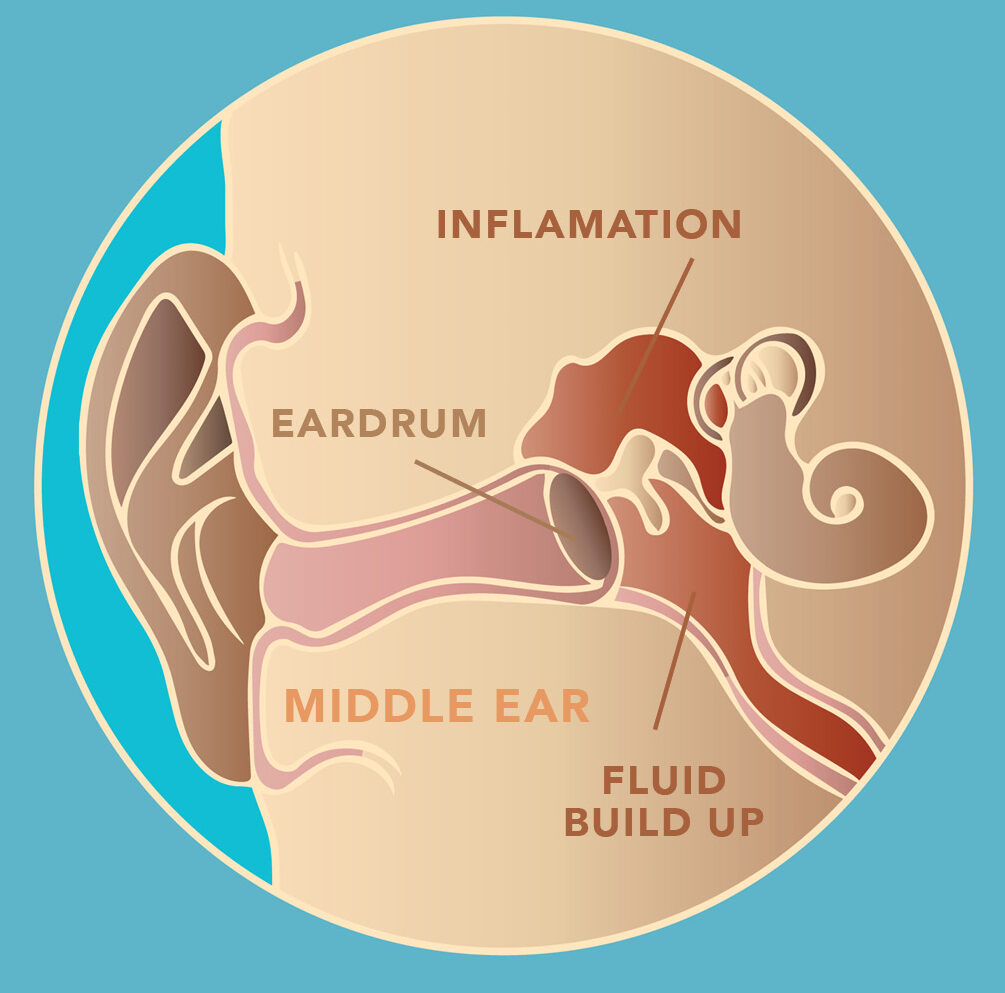
Ear infections can occur in the middle ear, outer ear, or inner ear. The most common type of ear infection is the middle ear infection, which occurs when fluid builds up in the space behind the eardrum due to the blockage of the Eustachian tube. This tube is responsible for draining fluid from the middle ear into the back of your throat.
When the Eustachian tube is blocked, fluid can't drain and can build up, causing infection. This blockage can be caused by a variety of factors, including allergies, a cold, sinus infections, smoking, or changes in air pressure.
Can Ear Infections Cause Jaw Pain?
Yes, ear infections can cause jaw pain. The jaw and the ear are connected by a network of nerves, which means that pain in one area can be felt in the other. In the case of an ear infection, the infection can cause inflammation and pressure on the nerve that connects the ear to the jaw, causing pain in both areas.
Additionally, the muscles in the jaw and around the ear can become tense as a result of the infection, further exacerbating the pain. In some cases, the pain may be severe enough to interfere with eating, speaking, and other daily activities.
What Are the Symptoms of Ear Infections?
The symptoms of ear infections can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. Common symptoms of middle ear infections include:
- Earpain
- Reduced hearing
- Fever
- Drainage from the ear
- Dizziness
Outer ear infections, also known as swimmer's ear, can cause symptoms such as:
- Earpain
- Itching or redness in the ear canal
- Swelling in the ear
- Drainage from the ear
In rare cases, inner ear infections can cause more severe symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and difficulty balancing.
How Are Ear Infections Diagnosed?
If you suspect you have an ear infection, it is important to see a doctor for a diagnosis. Your doctor will likely examine your ear with a special instrument called an otoscope to look for signs of infection, such as redness, fluid build-up, or pus.
In some cases, your doctor may also perform a hearing test to determine if the infection has affected your hearing. If the infection is severe or has lasted for a long time, your doctor may also order imaging tests such as a CT scan or MRI to check for complications.
How Are Ear Infections Treated?
The treatment for an ear infection will depend on the type and severity of the infection. In many cases, ear infections will clear up on their own within a few days to a week. Your doctor may recommend pain relievers such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen to help manage your symptoms.
If the infection is caused by bacteria, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to help clear the infection. It is important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if you start to feel better before the medication is finished.
In some cases, your doctor may need to drain fluid from the middle ear to relieve pressure and promote healing. This is done using a small tube called a myringotomy tube, which is inserted into the eardrum to help drain fluid from the middle ear.
Prevention Tips for Ear Infections
While ear infections can occur for a variety of reasons, there are steps you can take to help reduce your risk of developing an infection:
- Keep your ears clean and dry. Use a towel to dry your ears after swimming or showering.
- Avoid putting objects in your ears, such as cotton swabs or hair pins, which can damage the skin in the ear canal and increase your risk of infection.
- Avoid smoking and exposure to secondhand smoke, which can irritate the lining of the nose and throat and increase your risk of infection.
- Practice good hand hygiene to reduce the spread of germs that can cause infections.
The Bottom Line
While ear infections can be uncomfortable and even painful, the good news is that they are usually treatable with medication and resolve on their own within a few days or weeks. If you are experiencing ear pain or other symptoms of an infection, be sure to see a doctor for a diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By taking steps to protect your ears and practice good hygiene, you can help reduce your risk of developing an ear infection and alleviate associated jaw pain.
Image Sources
The following images were used in this article:
Can An Ear Infection Cause Jaw Pain? What To Know?

What a Middle Ear Infection Looks Like PhotoniCare