What Causes Uterine Cervix Cancer
As a woman, it may seem like there is no way to avoid the risks of cervical and endometrial cancers. However, it is important to understand the anatomical structures of the uterus and cervix, and how these structures can become cancerous. In this post, we will dive into the details of these conditions, exploring the causes, symptoms, and treatments.
Cervical Cancer
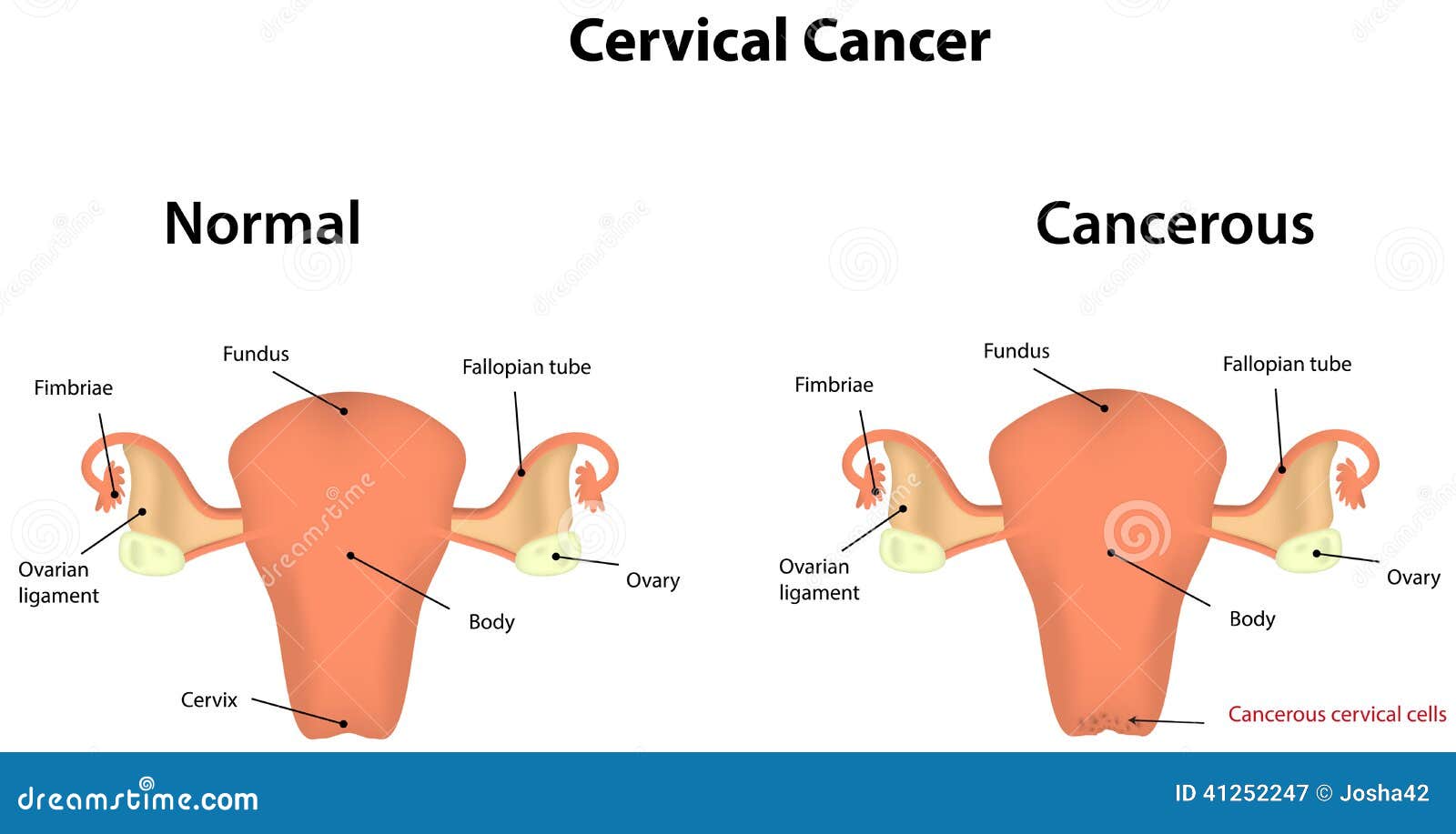
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that affects the cervix, which is the lower, narrow part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. This cancer develops when cells in the cervix become abnormal and grow rapidly. These abnormal cells can spread to other parts of the body, such as the vagina, bladder, rectum, or lungs if not treated promptly.
There are several factors that can increase the risk of developing cervical cancer, including:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Smoking
- Poor immune system
- Long-term use of birth control pills
- Having many sexual partners
- Having a previous history of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs)
Early symptoms of cervical cancer may include vaginal bleeding and pain during sex. As the cancer progresses, symptoms may include pelvic pain, abdominal swelling, and weight loss. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor immediately for diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment for cervical cancer may involve surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy, depending on the stage of cancer and other factors. It is important to work closely with your healthcare team to determine the best treatment plan for you.
Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial cancer is a type of cancer that affects the lining of the uterus, which is known as the endometrium. This cancer develops when the cells in the endometrium grow and multiply abnormally, often leading to the formation of a tumor. This type of cancer is most common in women who have gone through menopause.
Like cervical cancer, endometrial cancer can be caused by several factors, including:
- Obesity
- Increased levels of estrogen in the body
- Having never been pregnant
- Having a family history of endometrial cancer
Symptoms of endometrial cancer may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, or pain during sex. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see your doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment for endometrial cancer may involve surgery, radiation therapy, and hormone therapy, depending on the stage of cancer and other factors. It is important to work closely with your healthcare team to determine the best treatment plan for you.
Conclusion
It is important for women to be aware of the risk factors and symptoms of cervical and endometrial cancers. Regular gynecological check-ups and screenings can help detect these cancers in their early stages, when they are most treatable. By staying informed and taking preventative measures, women can minimize their risk of developing these types of cancers and ensure their overall health and well-being.