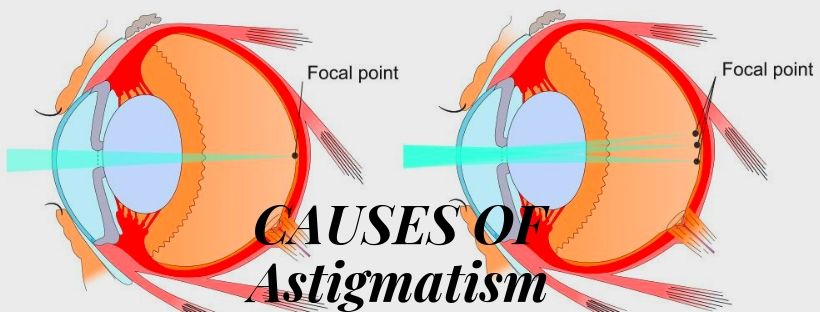
What Causes Worsening Astigmatism
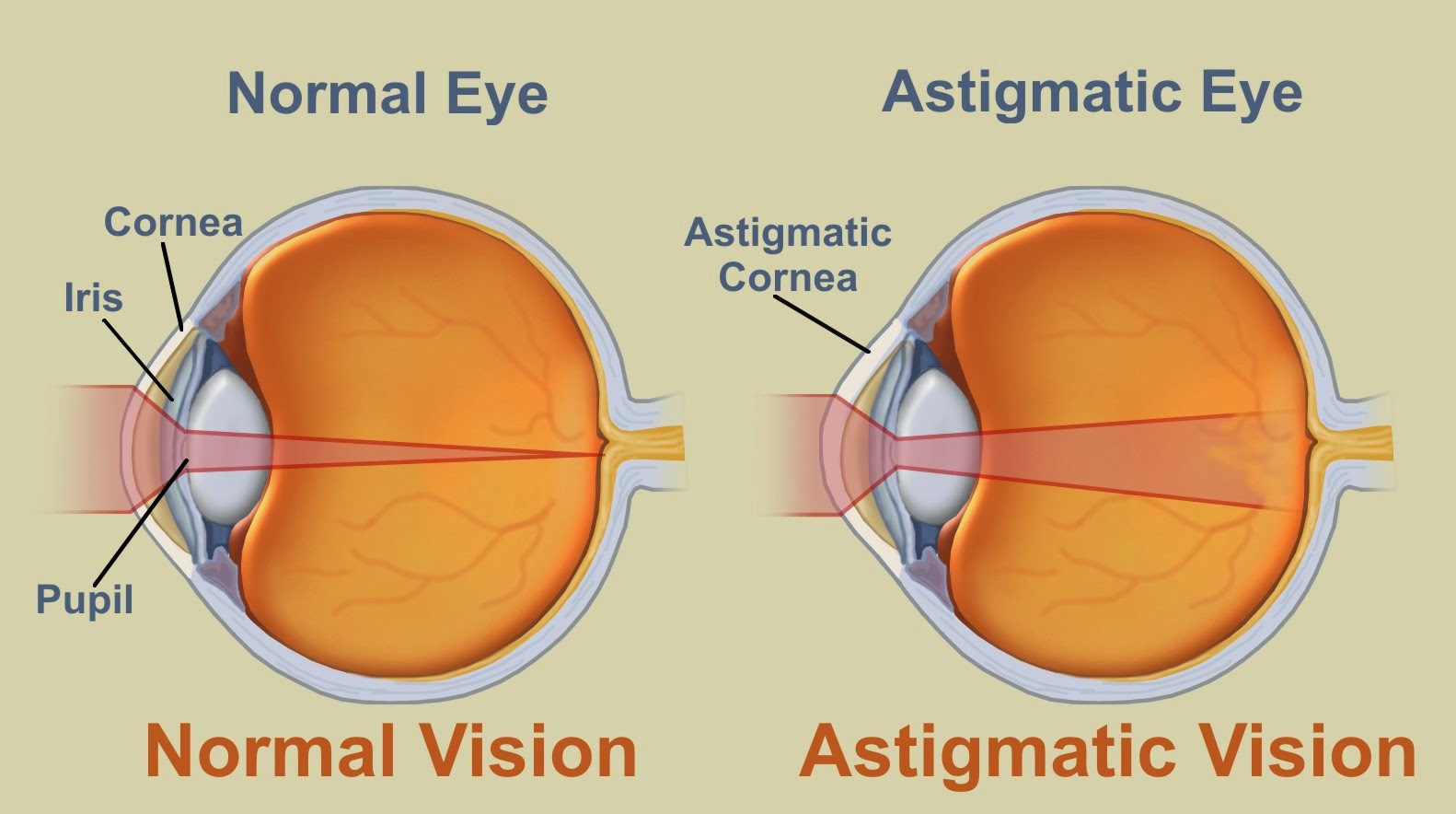
When it comes to vision issues, one common condition that people may encounter is astigmatism. This problem refers to an irregular shape of the cornea or lens that causes light to enter the eyes unevenly. As a result, people with astigmatism may experience blurred or distorted vision at both near and far distances. In this article, we will delve deeper into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of astigmatism.
Causes
Astigmatism can be either hereditary or acquired. Inherited astigmatism is caused by genetic factors and is often present at birth or begins to develop during childhood. Acquired astigmatism, on the other hand, can develop due to eye injuries, surgeries, or other eye diseases. There are also certain risk factors that may increase one's likelihood of developing astigmatism, including:
- Having a family history of the condition
- Being nearsighted, farsighted, or having a blurry vision
- Experiencing chronic eye fatigue or strain
- Having diabetes, keratoconus, or other eye-related disorders
Symptoms
Some of the most common symptoms of astigmatism include:
- Blurred or distorted vision, especially at night
- Eye strain or fatigue
- Headaches or migraines
- Sensitivity to light
- Squinting or tilting the head to see clearly
If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to consult an eye doctor for a thorough eye exam and diagnosis.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing astigmatism typically involves a comprehensive eye exam that tests for both visual acuity and the shape of the eye. Your eye doctor may perform various tests, including:
- Visual acuity test: This measures your ability to see and read letters at different distances.
- Corneal topography: This measures the shape of the cornea to detect any irregularities.
- Refraction test: This determines your prescription for corrective lenses (glasses or contacts) to correct your vision.
Treatment
The most common treatment options for astigmatism include corrective lenses, refractive surgery, and orthokeratology. Corrective lenses, such as glasses or contact lenses, can help to compensate for the irregular shape of the eye, allowing light to enter properly and improving vision. Refractive surgery, such as LASIK or PRK, can also be used to reshape the cornea and improve vision. Orthokeratology involves wearing a special type of contact lens overnight to temporarily flatten the cornea and correct vision during the day.
Prevention
While there is no surefire way to prevent astigmatism, there are some steps you can take to minimize your risk of developing the condition. These include:
- Getting regular eye exams and screenings
- Wearing protective eyewear during sports and other activities
- Taking frequent breaks when using computers or other screens
- Avoiding rubbing your eyes excessively
Conclusion
Astigmatism is a common vision problem that can cause blurred or distorted vision. It can be either hereditary or acquired and may develop due to eye injuries, surgeries, or other eye diseases. Some of the most common symptoms of astigmatism include blurred or distorted vision, eye strain or fatigue, headaches or migraines, sensitivity to light, squinting or tilting the head to see clearly. If you experience any of these symptoms, it's important to consult an eye doctor for a thorough eye exam and diagnosis. Treatment options for astigmatism include corrective lenses, refractive surgery, and orthokeratology. While there is no way to prevent astigmatism, there are some steps you can take to minimize your risk of developing the condition. By taking care of your eyes, you can help to maintain good vision for years to come.
References
Image Sources:
Astigmatism Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention Tips
Astigmatism Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Eyemantra