What Causes Acid Rain Short Answer
Acid rain is a type of precipitation that has a pH level lower than the average of normal rainfalls. This phenomenon is caused by natural sources such as volcanoes and wildfires, as well as human activities like the burning of fossil fuels. Acid rain is a serious environmental issue that impacts the earth's atmospheric and water systems all around the world. In this article, we will explore the definition, causes, and effects of acid rain in detail.
What is Acid Rain?
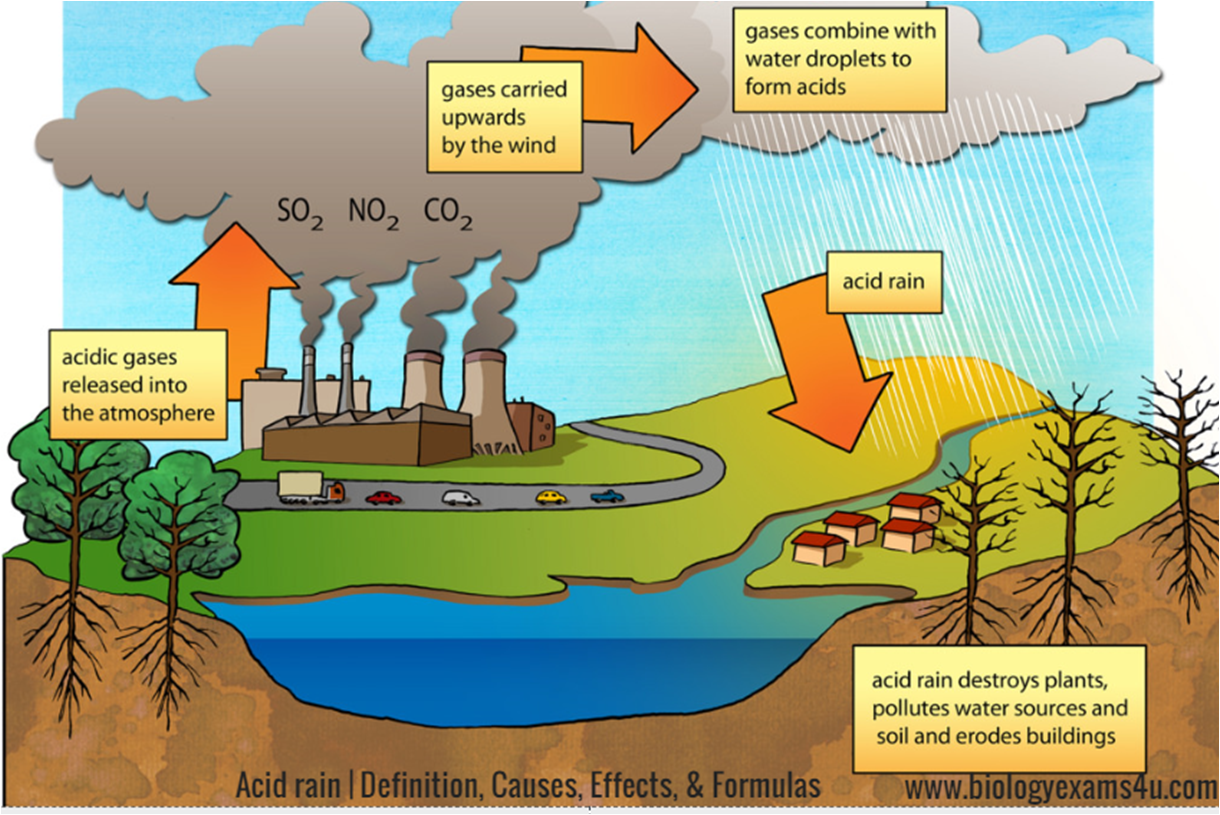
Acid rain is defined as a type of precipitation that contains high levels of acidic particles like sulfuric acid and nitric acid. The pH level of acid rain ranges from 4.3 to 5.6, which is lower than the pH level of ordinary rainwater. Acid rain is a type of atmospheric deposition, which means that the pollutants that cause acid rain are carried by the wind and deposited on the earth's surface through precipitation. The formation of acid rain is a result of chemical reactions that occur in the atmosphere between nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide and other pollutants.
Causes of Acid Rain
There are both natural and man-made causes of acid rain. Volcanoes, wildfires, and biological processes in the soil are natural sources of acidic particles that contribute to the formation of acid rain. However, the primary cause of acid rain is human activity, particularly the burning of fossil fuels in power plants, factories, and transportation. These activities lead to the release of nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide into the atmosphere, which undergo chemical reactions with other pollutants to form acidic particles.
Effects of Acid Rain
The effects of acid rain are wide-ranging and damaging to the environment, ecosystems, and human health. Acid rain has a detrimental impact on forests, lakes, and rivers. The acidic particles in rainwater can damage tree leaves, bark, and roots, making them more susceptible to disease and infestation. Acid rain also leads to the acidification of lakes and rivers, which can harm aquatic life and reduce biodiversity. The pH levels of soil can change due to acid rain, resulting in the destruction of soil nutrients that plants require to grow. Acid rain is also detrimental to human health, as inhaling acidic particles can lead to respiratory problems and other health issues.
Prevention of Acid Rain
Preventing acid rain requires a coordinated effort to reduce emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide. Governments and industries around the world have implemented regulations and policies to address the causes of acid rain. For example, power plants and factories have installed pollution control equipment to reduce emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide. In addition, the use of alternative energy sources like wind and solar power can help reduce the amount of fossil fuels burned and thereby reduce emissions of acidic particles.
Conclusion
Acid rain is a serious environmental issue that has far-reaching effects on the earth's ecosystems and human health. While the causes of acid rain are complex and varied, it is clear that human activity is the primary contributor to this problem. We must take steps to reduce emissions of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide to prevent the negative impact of acid rain. Hopefully, this article has helped you understand the definition, causes, and effects of acid rain, and why it is important to address this environmental issue.