What Are The Major Causes Of Eutrophication
Eutrophication is one of the most significant environmental issues affecting water bodies worldwide. It is a process in which an excessive supply of nutrients (such as nitrogen and phosphorus) to a water body causes excessive plant growth (algal blooms), leading to decreased oxygen levels in the water and ultimately, the death of aquatic life. Eutrophication is a natural process that occurs over many years, but human activities have accelerated it, leading to environmental damage and economic losses.
Causes of Eutrophication
There are various causes of eutrophication. One of the primary reasons is the discharge of untreated sewage and industrial effluent into water bodies. The high nutrient content in these effluents leads to excessive growth of aquatic plants and algae, which consume oxygen, leading to the death of aquatic life. Runoff from agricultural lands is another significant contributor to eutrophication. The use of fertilizers and manure in agriculture causes an increase in nutrient content, which eventually makes its way into water bodies through rivers and groundwater.
Deforestation is also a significant contributor to eutrophication. Trees absorb nutrients from the soil; when they are cut down, the nutrients are released into the soil, which eventually finds its way into water bodies. Climate change is another factor that aggravates eutrophication. Warmer temperatures result in increased algal growth, which leads to decreased oxygen levels and the death of aquatic life.
The Process of Eutrophication
Eutrophication occurs in three stages: nutrient enrichment, algal blooms, and oxygen depletion. In the first stage, nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphorus enter the water body, usually through human activities such as sewage discharge and agricultural runoff. The nutrients provide a food source for aquatic plants and algae, leading to their rapid growth (algal blooms) in the second stage.
The third stage occurs when the algae die and sink to the bottom of the water body, where they are consumed by bacteria. During the process of decomposition, the bacteria consume oxygen, leading to low oxygen levels in the water. The lack of oxygen in the water causes the death of aquatic life that requires oxygen to survive. The accumulation of dead plants and animals at the bottom of the water body results in the release of nutrients back into the water, starting the process again.
Examples of Eutrophication
The effects of eutrophication can be seen in various water bodies around the world. One example is the Black Sea, which has experienced severe eutrophication due to industrial and agricultural runoff. The excessive growth of algae has led to the formation of 'dead zones' in the sea, where oxygen levels are so low that aquatic life cannot survive.
Another example is Lake Erie in North America, which experienced severe eutrophication in the 60s and 70s due to industrial pollution and agricultural runoff. The lake became heavily polluted, and toxic algae blooms formed, leading to the death of aquatic life and economic losses in the tourism and fishing industries.
Prevention and Control of Eutrophication
Eutrophication is a preventable problem. The most effective way to control eutrophication is to prevent excessive nutrient inputs into water bodies. This can be achieved by various methods, such as treating sewage and industrial effluent before discharging into water bodies. The use of fertilizers and manure in agriculture should also be regulated, and alternative methods such as crop rotation and the use of organic fertilizers should be encouraged.
Another effective method is to reduce deforestation, which would help to prevent the release of nutrients into water bodies. Climate change is a significant challenge in fighting eutrophication, but reducing carbon emissions can help mitigate its effects.
Conclusion
Eutrophication is a global environmental issue affecting water bodies worldwide. It is caused by excessive nutrients entering water bodies from human activities such as sewage discharge, agricultural runoff, and deforestation. The effects of eutrophication can be seen in various water bodies worldwide, leading to economic losses and environmental damage. Preventing eutrophication requires the regulation of human activities that lead to excessive nutrient inputs into water bodies, promoting alternative methods in agriculture, reducing deforestation, and mitigating climate change through reducing carbon emissions. By implementing these measures, we can prevent eutrophication and ensure the health of our water bodies and the life that depends on them.
Images

Figure 1. Was ist Eutrophication? WorldAtlas
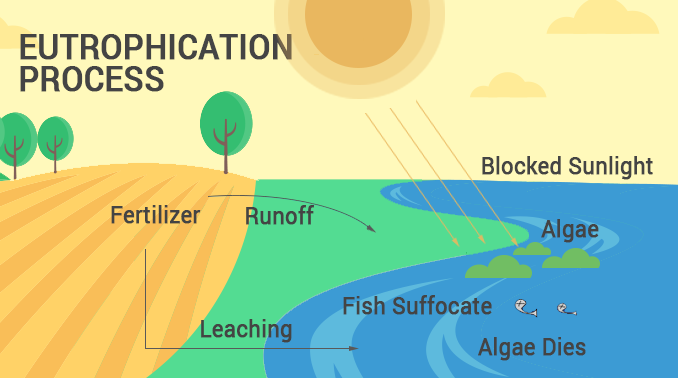
Figure 2. How Does Eutrophication Work? Causes, Process, and Examples Earth How