What Can Cause Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
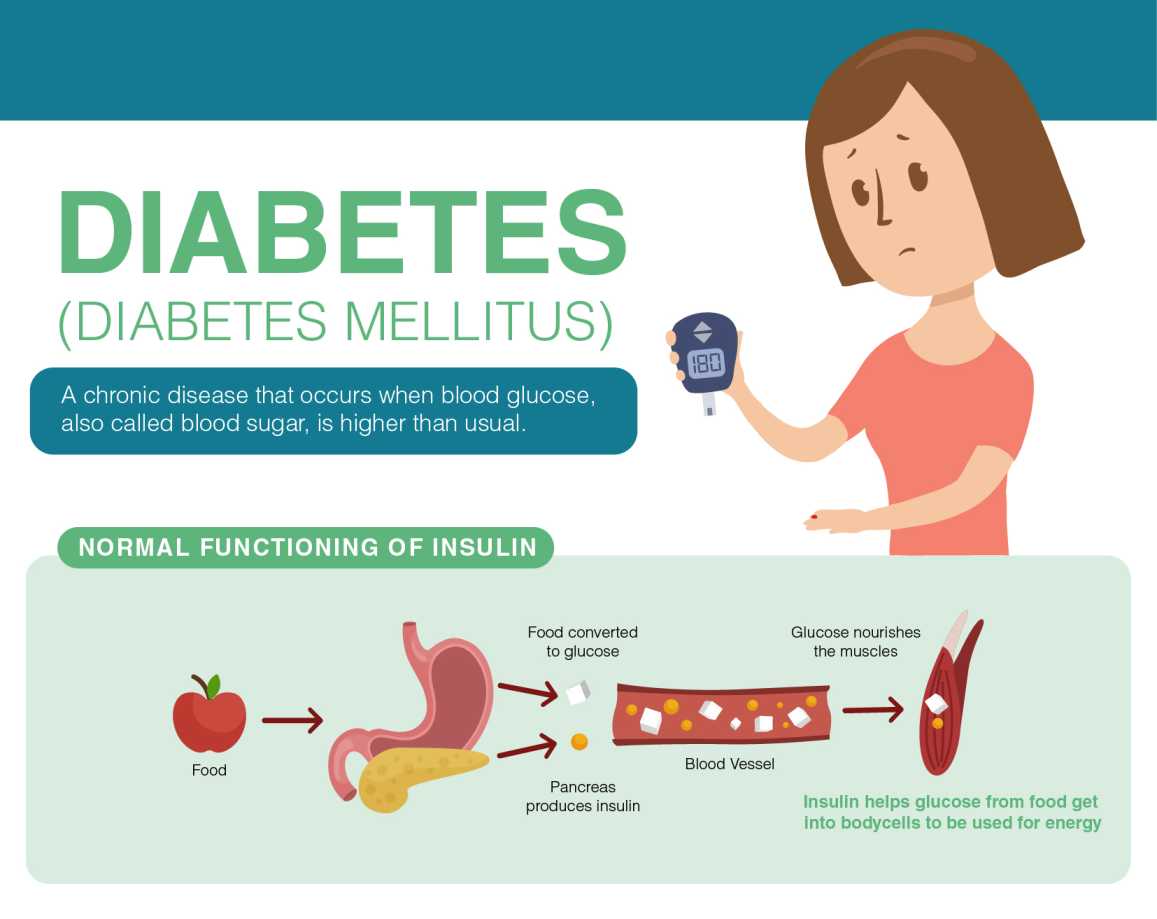
Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels over a prolonged period of time. There are various types of diabetes mellitus, with type 1 and type 2 being the most common. The causes of diabetes mellitus vary depending on the type, with type 1 being an autoimmune disease and type 2 being caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. The management and treatment of diabetes mellitus depends on the type and severity of the condition.
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 diabetes mellitus, also known as juvenile diabetes, is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system attacks the pancreas, leading to an inability to produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels, and without it, blood sugar levels can become dangerously high. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is typically diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, and requires lifelong insulin therapy.
Type 2 diabetes mellitus is the most common type, accounting for over 90% of all cases of diabetes. It is caused by a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors, such as obesity and physical inactivity. In type 2 diabetes mellitus, the body produces insulin, but is unable to use it effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes mellitus can often be managed through lifestyle changes and medication, although some people may require insulin therapy.
Risk Factors and Causes of Diabetes Mellitus
There are several risk factors and causes of diabetes mellitus. Some of the most common risk factors for type 2 diabetes include obesity, physical inactivity, poor diet, and a family history of the condition. Other risk factors include age, ethnicity, and a history of gestational diabetes during pregnancy.
The causes of type 2 diabetes mellitus are complex, and involve a combination of genetic and lifestyle factors. Genetics play a role in determining an individual's susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus, but lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and a poor diet are also major contributing factors.
Exercise for Diabetes Mellitus Management
Exercise is an important component of diabetes mellitus management. Regular physical activity can help control blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce the risk of complications associated with diabetes mellitus. It is recommended that individuals with diabetes mellitus engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, spread over at least three days per week with no more than two consecutive days without physical activity.
Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
The treatment of diabetes mellitus depends on the type and severity of the condition. In type 1 diabetes mellitus, insulin therapy is required for life. In type 2 diabetes mellitus, the initial treatment may involve lifestyle changes such as diet and exercise, as well as medication to help lower blood sugar levels. In some cases, insulin therapy may be required.
There are also several other treatment options for diabetes mellitus, such as continuous glucose monitoring, insulin pumps, and pancreas transplants. These treatments are typically reserved for people with severe or uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
Conclusion
Diabetes Mellitus is a serious health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the types, causes, and risk factors of diabetes mellitus is essential for effective management and treatment. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and following a healthy diet are important lifestyle factors that can help prevent or manage diabetes mellitus. If you suspect that you may have diabetes mellitus, it is important to speak with your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.