What Causes Adhd In A Child
If you’re curious about the inner workings of the human brain and its complex composition, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a fascinating topic to delve into. ADHD is a neurodevelopmental condition that is characterized by hyperactivity, lack of focus, and impulsive behavior. It affects people at an early age and persists throughout their lives. While ADHD is one of the most frequently diagnosed neurological disorders in children and adults, it remains an enigma for many people.
Exploring ADHD
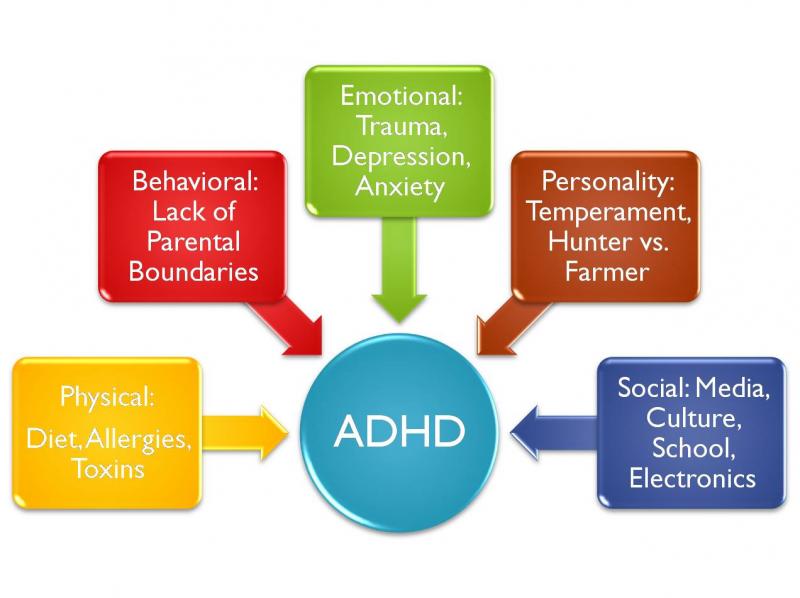
ADHD has been classified as an executive function disorder. This means that it affects the normal process of carrying out complex tasks such as problem-solving, planning, and focusing attention. The exact cause of ADHD is not known, but there are various factors linked to it. Studies have shown that ADHD is hereditary, and if a child's parents have ADHD, there's a higher chance of that child developing the disorder.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/adhd-attention-deficit-hyperactivity-disorder-included-definition-symptoms-traits-causes-treatment-5084784_final-bc92546bc9df465ea7f13fc423c2085b.jpg)
Research has also shown that ADHD is linked to certain chemical imbalances in the brain. The neurotransmitters that regulate behavior, mood, and attention levels are affected by these imbalances. The resulting disruption in normal signals causes the symptoms of ADHD.
ADHD Symptoms
Symptoms of ADHD can vary, but they typically present as an inability to focus, restlessness, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. ADHD can be divided into three subtypes:
- Inattentive Type - this type of ADHD is characterized by a lack of focus and distractibility. Individuals with this type may have trouble keeping track of personal items or completing tasks on time.
- Hyperactive-Impulsive Type - this type is characterized by hyperactivity, impulsivity, and short attention span. Individuals with this type may struggle to sit still, interrupt others while speaking and have trouble waiting for their turn.
- Combined Type - this form of ADHD combines the symptoms of both Inattentive and Hyperactive-Impulsive types.
The symptoms of ADHD can be challenging for individuals to manage, but treatments such as medication and behavioral therapy can help alleviate the symptoms and enable people to lead productive lives.
Treatment for ADHD
Treating ADHD is a complex and varied process and differs from individual to individual. A combination of medication and therapy is often used to manage the symptoms. Stimulant medications such as Ritalin and Adderall are most commonly prescribed to manage the disruptive symptoms of ADHD. While these drugs can be effective, they also have potential side effects and can be habit-forming.
Behavioral therapy is also essential in treating ADHD. This therapy focuses on teaching people how to manage their symptoms in ways that can be applied to different situations and contexts. Behavioral therapy may include teaching social skills, emotional regulation, and time management techniques.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early diagnosis of ADHD is critical to helping people manage the disruptive and challenging symptoms. Unfortunately, because the symptoms of ADHD can overlap with other behavioral disorders, diagnosis can be challenging. However, if you suspect that you or your child has ADHD, it is important to consult with a healthcare provider to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
In summary, ADHD is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach to diagnosis and treatment. While symptoms may present at an early age and persist throughout adulthood, interventions such as medication and behavioral therapy can help to manage the condition and improve the quality of life for individuals living with ADHD.