What Is Diabetes Ketones
The human body is a system that is highly regulated and complex. A key component of this system is blood sugar, which is regulated by insulin. Insulin is a hormone that is produced by the pancreas and plays a crucial role in balancing blood sugar levels. However, when the body is unable to produce insulin or when there is a problem with insulin functioning, blood sugar levels can become dangerously high. This condition is known as diabetes.
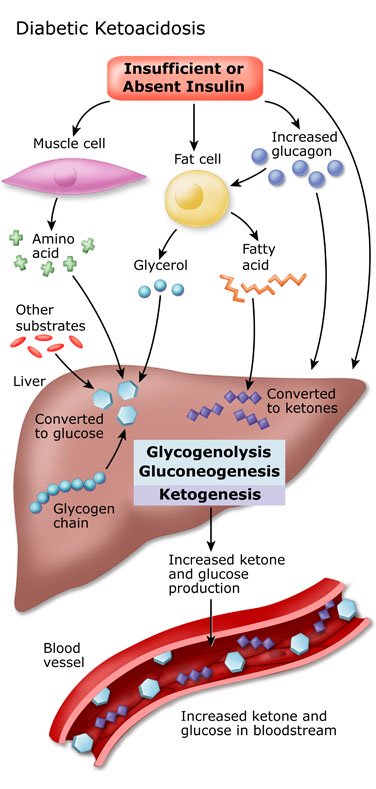
What is Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) is a life-threatening complication of diabetes that occurs when the body starts breaking down fat for energy instead of glucose. This results in the buildup of ketones in the blood, which can make the blood acidic. DKA can occur in people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, but it is more common in people with type 1 diabetes. It is a medical emergency that requires prompt treatment to avoid serious complications.
What Causes Diabetic Ketoacidosis?
DKA is usually caused by a lack of insulin or by insulin resistance. Without enough insulin, the body cannot use glucose for energy and instead starts to break down fat for energy. This process releases ketones, which build up in the blood and make it acidic.
Other factors that can lead to DKA include:
- Infection
- Skipping insulin doses
- Illness or injury
- Emotional or physical stress
- Pregnancy
Signs and Symptoms of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
The symptoms of DKA usually develop over a period of several hours to a few days. Some of the common symptoms include:
- High blood sugar levels
- Frequent urination
- Extreme thirst
- Dry mouth and skin
- Weakness or fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Deep, rapid breathing
- Sweet, fruity breath
Treatment of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
DKA is a medical emergency and requires prompt treatment in a hospital. Treatment usually involves:
- Intravenous fluids to replace fluids lost through frequent urination and vomiting
- Insulin therapy to lower blood sugar levels and stop the production of ketones
- Electrolyte replacement to restore the balance of minerals in the body
- Treatment of any underlying conditions, such as infection or injury
Preventing DKA involves keeping blood sugar levels within a specific target range, taking insulin as prescribed, eating a balanced diet, and monitoring blood sugar levels regularly.
Conclusion
Diabetic ketoacidosis is a serious complication of diabetes that can be life-threatening if left untreated. It is important to recognize the signs and symptoms of DKA and seek prompt medical attention if they occur. With proper treatment and prevention, DKA can be managed effectively and the risk of complications can be reduced.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when the pancreas produces little or no insulin. It is an autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. People with type 1 diabetes require insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage their blood sugar levels.
Some of the common symptoms of type 1 diabetes include:
- Increased thirst and urination
- Excessive hunger
- Weight loss
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
- Irritability
There is no cure for type 1 diabetes, but it can be managed effectively with proper treatment and self-care.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis SimplifiedMed!
SimplifiedMed is a website dedicated to simplifying medical concepts and making them easier to understand for everyone. One of the topics that SimplifiedMed covers is diabetic ketoacidosis. The website explains DKA in simple terms and provides helpful information on how to recognize and treat this condition.
By providing easy-to-understand information on medical conditions like DKA, SimplifiedMed aims to empower people to take control of their health and make informed decisions about their healthcare.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with diabetes or is at risk of developing DKA, it is important to stay informed and take proactive steps to manage and prevent complications.