What Cause Gallbladder Cancer
Gallbladder cancer is a rare type of cancer that usually begins in the lining of the gallbladder and spreads to other areas of the body. Though it is uncommon, it is important to learn more about this cancer as it can be life-threatening. Here's all you need to know about gallbladder cancer, its types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment.
Gallbladder Cancer Types
There are different types of gallbladder cancers, depending on the cells from which they originate. The types of gallbladder cancer are:
- Adenocarcinoma
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- Small cell carcinoma
- Other rare types, such as lymphoma and sarcoma
Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of gallbladder cancer, which arises from the gland cells present in the inner lining of the gallbladder.
Causes of Gallbladder Cancer
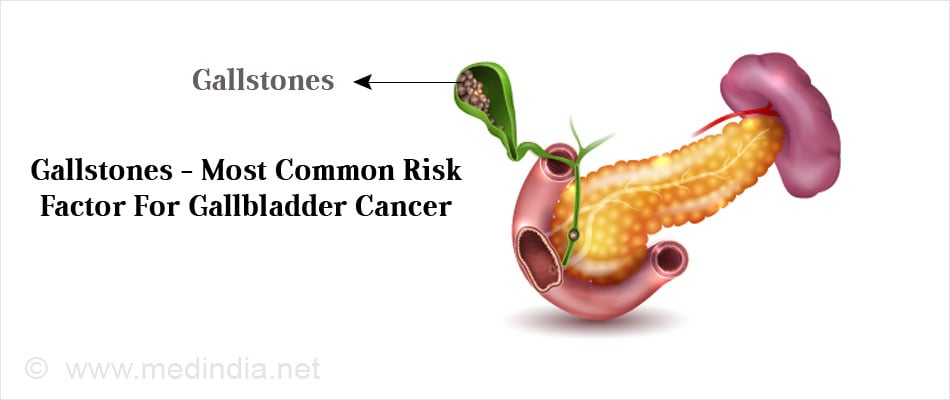
The exact cause of gallbladder cancer is unknown. However, certain factors may increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer, including:
- Gallstones: People with a history of gallstones have a higher risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
- Age and gender: Gallbladder cancer is more common in older adults and women.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder: Inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis) can increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
- Family history: People with a family history of gallbladder cancer are at a higher risk of developing the disease.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese may increase the risk of developing gallbladder cancer.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Cancer
Gallbladder cancer doesn't usually cause any symptoms in the early stages. However, as the cancer progresses, the following symptoms may develop:
- Abdominal pain: The pain usually occurs in the upper right side of the abdomen and may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Jaundice: Jaundice is a condition that causes yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pale stools and dark urine
- Loss of appetite
- Fever and chills
Diagnosis of Gallbladder Cancer
If gallbladder cancer is suspected, the following tests and procedures may be done to diagnose the condition:
- Abdominal ultrasound: An ultrasound uses sound waves to create pictures of the gallbladder and the surrounding organs.
- CT scan: A CT scan uses X-rays to create detailed images of the inside of the body.
- MRI: An MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create pictures of the inside of the body.
- Biopsy: A biopsy involves taking a small sample of the tissue from the gallbladder for examination under a microscope.
Treatment of Gallbladder Cancer
The treatment options for gallbladder cancer depend on the stage of cancer and the patient's overall health. The treatment options include:
- Surgery: Surgery is the most common treatment for gallbladder cancer. It involves removing the gallbladder and any surrounding tissues that are affected by cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is a treatment that involves using drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy involves using high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells.
In conclusion, gallbladder cancer is a rare but serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. It is important to know the symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options for gallbladder cancer to take preventive measures and receive treatment if diagnosed with the disease.