What Causes Suppurative Appendicitis
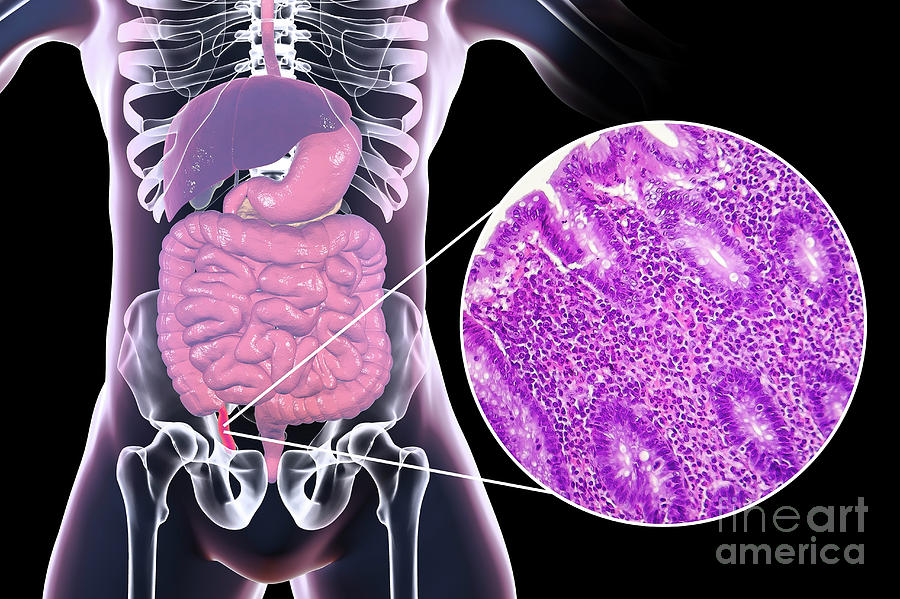
Acute suppurative appendicitis is a condition that affects numerous individuals across the globe, especially in Asian regions. This condition tends to cause inflammation in the appendix, which is a small, tube-like structure present within the lower right part of the abdomen. The inflammation results in the accumulation of pus and can be quite painful, often requiring immediate medical attention.
Calcified Parasites Found in Acute Suppurative Appendicitis
In some cases, acute suppurative appendicitis is found to be associated with the presence of calcified parasites. These parasites are believed to enter the appendix through the fecal matter, which can cause blockages in the appendix. Over time, the blockages can lead to inflammation and the accumulation of pus. The presence of calcified parasites is often identified through radiographic imaging techniques.

The exact cause of the migration of these parasites from the intestines to the appendix is not yet fully understood. Some studies suggest that the accumulation of fecal matter in the appendix may provide a favorable environment for the growth and development of parasites, leading to their migration into the structure.
Symptoms of Acute Suppurative Appendicitis
The symptoms of acute suppurative appendicitis can vary depending on the severity of the condition. However, some common signs and symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain, which usually starts near the navel and spreads to the lower right area of the abdomen.
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
- Bloating and gas
- Diarrhea
If you experience persistent abdominal pain or any of the above-mentioned symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Treatment Options for Acute Suppurative Appendicitis
The conventional treatment for acute suppurative appendicitis is surgical removal of the inflamed appendix, which is known as an appendectomy. The surgery is performed under general anesthesia and involves making small incisions in the abdomen, through which a laparoscope and other surgical instruments are inserted to remove the appendix.
In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection and inflammation associated with acute suppurative appendicitis. However, antibiotics alone are not always considered a reliable treatment option and are usually used as an additional measure along with surgery.
Preventive Measures for Acute Suppurative Appendicitis
While there is no definite way to prevent the occurrence of acute suppurative appendicitis, some preventive measures may help in reducing the risk of developing the condition. These measures include:
- Eating a healthy, fiber-rich diet that includes fresh fruits and vegetables
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids
- Maintaining good personal hygiene
- Avoiding the consumption of contaminated food and water
- Seeking prompt medical attention if you experience any symptoms associated with acute suppurative appendicitis
Conclusion
Acute suppurative appendicitis is a painful condition that affects numerous individuals across the globe. While the precise cause of this condition remains uncertain, the presence of calcified parasites is a common finding associated with it. Seeking prompt medical attention and undergoing surgical removal of the inflamed appendix is the primary mode of treatment for this condition. Additionally, adopting preventive measures such as maintaining good personal hygiene, eating a healthy diet, and staying hydrated may help in reducing the risk of developing acute suppurative appendicitis.
Overall, it is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms associated with acute suppurative appendicitis and seek medical attention promptly if you experience any of them. This condition can be treated effectively if diagnosed early and can lead to significant complications if left untreated.