What Causes Bronchitis Asthma
Asthma and bronchitis are two respiratory diseases that have similar symptoms but differ in some important ways. They can often be mistaken for one another, but it is important to understand the differences in order to properly diagnose and treat these conditions.
Understanding Asthma
Asthma is a chronic respiratory disease that affects the airways in the lungs. It is characterized by inflammation and narrowing of the airways, making it difficult to breathe. Symptoms include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. Asthma symptoms can be triggered by a variety of factors, including allergens, exercise, and stress.
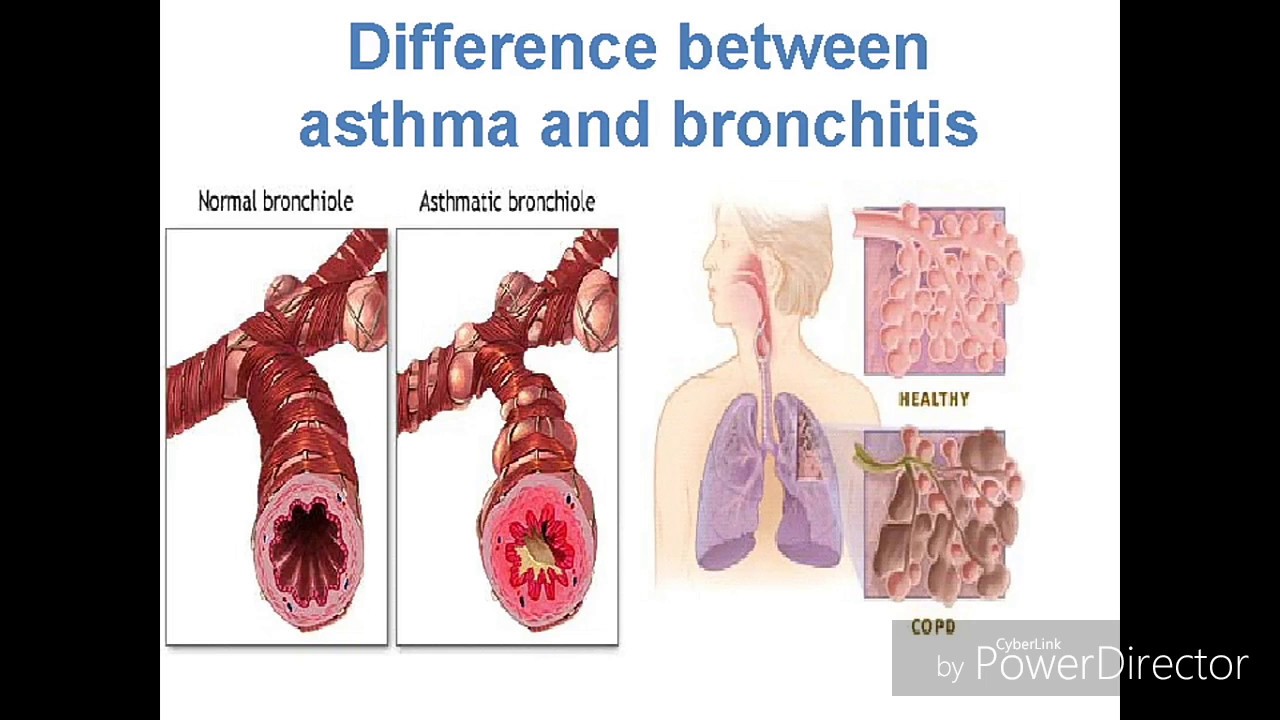
Asthma is a complex condition that is affected by multiple factors, including genetics, environment, and lifestyle. It is typically diagnosed through a series of tests, including lung function tests, allergy tests, and imaging studies.
Understanding Bronchitis
Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the air passages that lead to the lungs. It is typically caused by a viral or bacterial infection and can be acute or chronic. Symptoms include coughing, chest discomfort, and production of mucus. Bronchitis can be contagious and is often spread through coughing or sneezing.

Unlike asthma, bronchitis is typically treated with antibiotics rather than anti-inflammatory medications. Acute bronchitis usually resolves on its own within a few weeks, but chronic bronchitis can lead to long-term damage to the lungs.
The Differences Between Asthma and Bronchitis
While asthma and bronchitis share some common symptoms, there are several key differences between the two conditions:
- Asthma is a chronic condition, while bronchitis is usually acute or chronic
- Asthma is typically treated with anti-inflammatory medications, while bronchitis is usually treated with antibiotics
- Asthma symptoms are often triggered by allergens, exercise, and stress, while bronchitis symptoms are typically caused by viral or bacterial infections
- Asthma is typically diagnosed through a series of tests, while bronchitis is often diagnosed clinically based on symptoms and physical examination
It is important to seek medical attention if you are experiencing symptoms of asthma or bronchitis. Your doctor can help determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Treatment for Asthma and Bronchitis
The treatment for asthma and bronchitis varies depending on the severity and underlying cause of the condition. In general, treatment for asthma may include:
- Inhaled medications, such as bronchodilators and corticosteroids, to reduce inflammation and open up the airways
- Lifestyle modifications, such as avoiding triggers and practicing good asthma management techniques
- Allergy immunotherapy, in some cases
Treatment for acute bronchitis may include:
- Over-the-counter medications, such as cough suppressants and pain relievers
- Antibiotics, if the infection is bacterial
- Rest and plenty of fluids
Chronic bronchitis may require ongoing treatment with medications and lifestyle modifications, such as quitting smoking and avoiding lung irritants.
Conclusion
Asthma and bronchitis are two respiratory diseases that share some common symptoms but differ in important ways. If you are experiencing symptoms of either condition, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Whether you are living with asthma, bronchitis, or another respiratory condition, it is important to practice good self-care and follow your treatment plan to manage your symptoms and prevent complications.